Quickstart
The Cloudmesh Compute Cluster service allows you to execute analytical, computational workflows which run programs on remote compute resources. We specify not only a list of tasks to be executed, but the tasks can also have dependencies between each other expressed through a direct, cyclic graph. Currently, we have predefined task types that can execute shell scripts, Python programs, and Python notebooks, all of which can be executed on local or remote compute resources.
In Figure 1 we depict a simple example workflow to be executed where each task is executed sequentially. The status of the execution can be displayed as table or as graph. In Figure 1, we showcase how the graph changes its appearance over time.
Step 0 |
Step 0.5 |
Step 1 |
Step 2 |
Step 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Definition |
Running first task |
Finished first task |
Finished second task |
Completed workflow |
Figure 1: Execution and display graph of an example workflow over time
We can specify such workflows in a YAML file making it very easy to create and manage them. To get you started, we have developed a quickstart example that you can enhance to get acquainted with the system.
Once a workflow is specified, it can be executed a using one of our interfaces. This includes a Python API and a command line interface without a REST service. In addition we have, with the help of the Python API, developed a REST service so that integration into other frameworks can be facilitated through REST calls. The availability of the REST service is important to access it from non Python frameworks, but also allows the easy interaction through a Web-based Portal.
Let us demonstrate a number of selected features with the help of this quickstart. We will only focus on using the REST service.
Setup
To start, the code is needed and we assume you are standing in the cloudmesh-cc directory. Use the following commands
git clone https://github.com/cloudmesh/cloudmesh-cc.git
cd cloudmesh-cc
pip install -e .
We also assume you start the service with
cms cc start --reload
Creating a simple example
First let us create a simple workflow example that we already have included for you in our source code. We will use this workflow and copy it into a temporary directory:
mkdir -p /tmp/workflow-example
cp tests/workflow-example/workflow-example.yaml /tmp/workflow-example
cp tests/workflow-example/*.sh /tmp/workflow-example
We like you to inspect the example so you get an overview of how to define a workflow that is located in GitHub: and is located in the folder tests/workflow-example/
Now we can test a selected number of ways on how to interact with the service. We showcase here how to
upload workflows as tar/xz file of a self containing directory, or
upload all files in a directory recursively
A. Upload and run a workflow embedded in an archive file
We can upload an archive file which contains all the workflow files,
including the yaml specification file and the scripts. Providing an
archive file such as a .tar, .tar.gz, or .xz. may enable the
workflow to be better suited towards portability and simplicity, where
one can share an archive file with another user. We will choose here a
tar file as example.
Create tar archive file
Before uploading a tar archive file, we must first create it using
the previous example yaml and scripts that we copied.
tar -C /tmp/workflow-example -cf workflow-example.tar .
Option 1: Upload via curl
We can upload the archive file by using the curl terminal command as
follows:
curl -X 'POST' \
'http://127.0.0.1:8000/workflow?archive=workflow-example.tar' \
-H 'accept: application/json' \
-d ''
Option 2: Upload via /docs
As the service is using also an OpenAPI 2.0 specification the workflow
can also be uploaded implicitly through the specification GUI. Navigate
to http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs and use the POST Upload method.
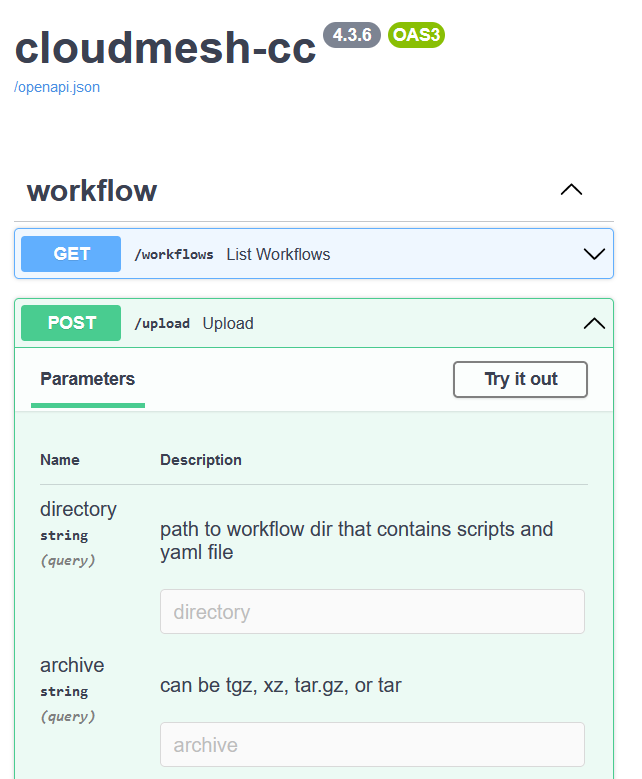
Fig. 1 Browser API GUI for Cloudmesh Compute Cluster
Please click Try it out and then enter
~/cm/cloudmesh-cc/workflow-example.tar in the archive field and
then click Execute.
Option 3: Upload via the Python API
As we use a REST service, we can also easily upload the workflow through a Python enabled REST call. We will use Python requests to demonstrate this upload feature.
import requests
r = requests.post('http://127.0.0.1:8000/workflow?archive=workflow-example.tar')
print(r)
print(r.text)
Printing r returns the response code from the API (a code of 200
indicates success). Printing r.text returns the message from the
API, such as a success or error message.
Option 4: Upload with a third party REST framework
Naturally if you like to use a different REST API you can do so. You can also use different programming languages and we leave it up to you to choose the framework of your choice to interact with the REST service, popular choices are JavaScript, Go, C/C++, matlab, and R, to name a few.
B. Upload a dir that contains workflow directory
To increase flexibility and allow quick experiments, users can specify a workflow directory which contains the yaml specification file and the scripts. This way, pre-archival of the directory is not needed. The program sets up the workflow by copying the necessary files from the specified directory.
There are three different ways to upload the dir: via curl on the
command line, via the browser GUI, and via the Python API.
Option 1: Upload via curl
A workflow can be uploaded easily with a curl command from the command line. On the command line execute:
curl -X 'POST' \
'http://127.0.0.1:8000/workflow?directory=~/cm/cloudmesh-cc/tests/workflow-example' \
-H 'accept: application/json' \
-d ''
Option 2: Upload via /docs
Also here one can upload the needed files with the OpenAPI
specification interface on the service. Navigate to
http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs and use the POST Upload method.
Click Try it out and then enter ~/cm/cloudmesh-cc/tests/workflow-example in the
directory field and then click Execute.
Option 3: Upload via the Python API
Accessing the upload from the Python API is very easy. We will use python requests to demonstrate the upload of the workflow.
import requests
r = requests.post('http://127.0.0.1:8000/workflow?directory=~/cm/cloudmesh-cc/tests/workflow-example')
print(r)
print(r.text)
Printing r returns the response code from the API (a code of 200
indicates success). Printing r.text returns the message from the
API, such as a success or error message.
Parameters to the Upload a workflow with a REST call
The upload REST URL can take different parameters, such as
?directory=name?archive=name.tar.gz?archive=name.tgz?archive=name.xz?yaml=name
The semantic of the upload is specified through its parameter. Only one of them can be used at a time.
The directory parameter indicates that the contents of a specified directory will be transferred into a workflow.
The archive parameter indicates that an archive file, such as a tar
file, will be extracted and its contents will be transferred into a
workflow. Please note that the archive and directory parameters
can not be used in the same REST call.
The yaml parameter indicates that only a yaml file will be uploaded
without any corresponding scripts. Uploading a yaml file by itself
allows for a script specified by the yaml to be uploaded later. The yaml
can even work without scripts by using the exec specification within
the yaml.
Run the workflow
To run, navigate to homepage at http://127.0.0.1:8000/ and click the
workflow-example on the left side. Then click Run.