Apache Hadoop YARN¶
YARN is a framework for job scheduling and cluster resource management to support Hadoop 2 with generic applications. Upgraded Hadoop is not just simply tied with a MapReduce application for data processing. It can support MPI (mpich2-yarn), graph processing(Apache Giraph, Google Pregel) in a Hadoop YARN cluster.
Tip
Duration 1 hour
Overview¶
Apache Software Foundation (ASF) defines YARN as the next generation of MapReduce or MapReduce 2.0 (MRv2). The main change of MRv2 is the resource management from the programming model of MapReduce. The MRv2 consists of a single master ResourceManager (RM), one slave NodeManager (NM) per cluster-node, and ApplicationMaster (AM) per application. Under YARN, MapReduce is independent as it behaves like a type of available application running in a YARN container. YARN is an abbreviation for Yet Another Resource Negotiator which was addressed in January 2008 from https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/MAPREDUCE-279
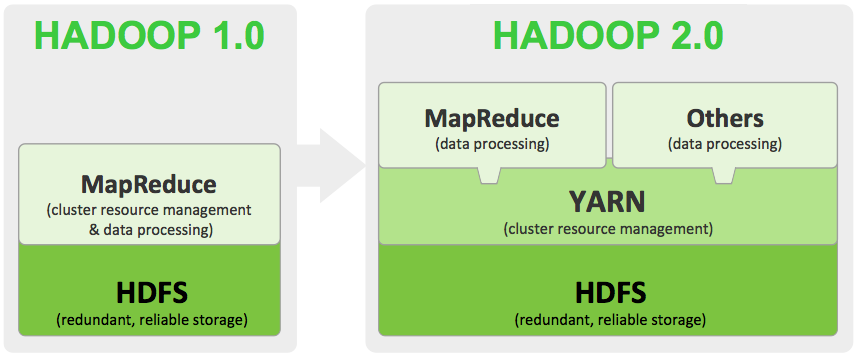
Figure 1. Changes of Hadoop v1 to v2 (image source: http://media.bestofmicro.com/X/8/430172/original/yarn.png)
Hadoop v1¶
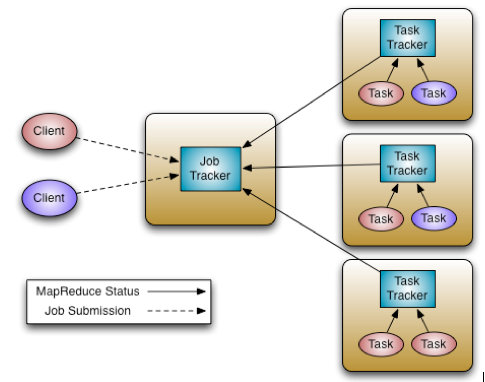
Figure 2. Hadoop v1 Architecture (image source: http://hortonworks.com/blog/apache-hadoop-yarn-background-and-an-overview/)
- JobTracker from MR1 splits up two parts: RM, AM(job scheduling/monitoring).
- ResourceManager (RM) consists of Scheduler, ApplicationsManager (ASM).
- ASM is to manage each MapReduce job and terminated when the job completes.
- JobHistoryServer records completed jobs.
Hadoop v2¶
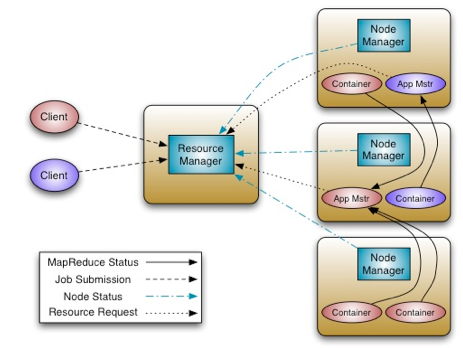
Figure 3. Hadoop v2 Architecture (image source: http://hadoop.apache.org/docs/current/hadoop-yarn/hadoop-yarn-site/YARN.html)
Configuration¶
- YARN configuration options, which go in yarn-site.xml
- MapReduce configuration options, which go in mapred-site.xml.
Benefits of changing MR1 to MR2¶
- by breaking up the JobTracker into a few different services, it avoids many of the scaling issues facing MR1.
- Most important, it makes it possible to run frameworks other than MapReduce on a Hadoop cluster. For example, Impala can also run on YARN and share resources on a cluster with MapReduce.
ResourceManager (RM)¶
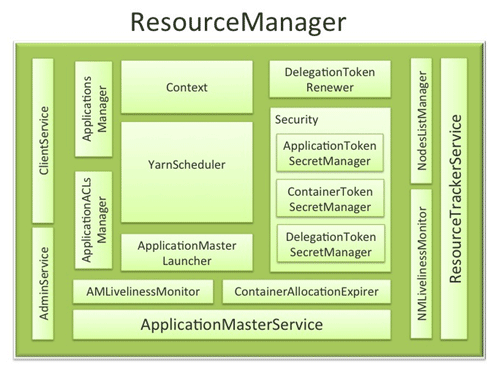
Figure3. ResourceManager Components (image source: http://hortonworks.com/blog/apache-hadoop-yarn-resourcemanager/)
Scheduler¶
The Scheduler is responsible for allocating resources to the various running applications subject to familiar constraints of capacities, queues etc. The scheduler is responsible for deciding which tasks get to run where and when to run them. Capacity - Allocates resources to pools, with FIFO scheduling within each pool. The CapacityScheduler supports hierarchical queues to allow for more predictable sharing of cluster resources Fair - Allocates resources to weighted pools, with fair sharing within each pool. llocates resources based on arrival time.
ApplicationsManager (ASM)¶
The second part of the Resource Manager, called the Application Manager, receives job submissions and manages to launch the Application Master. The Application Manager handles failures of the Application Master, while the Application Master handles failures of job containers. The Application Master then is really an application-specific container charged with management of containers running the actual tasks of the job.
Resource Container memory, cpu, disk, network etc.
Map-Reduce schedulers¶
- CapacityScheduler
- FairScheduler
NodeManager (NM)¶
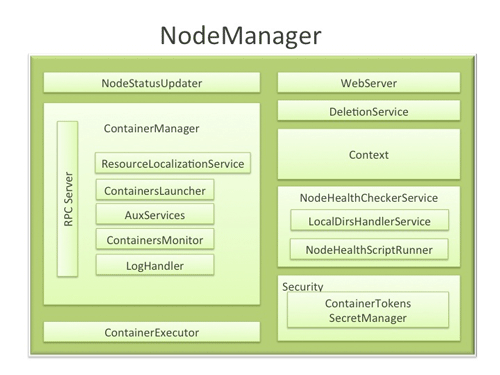
Figure4. NodeManager Components (image source: http://hortonworks.com/blog/apache-hadoop-yarn-nodemanager/)
NodeManager (NM) is a YARN service that manages resources and deployment on a cluster node. NM is separated from TaskTracker from MR1 and now NM is responsible for launching containers, each of which can house a map or reduce task. NM is YARN’s per-node agent and takes care of the individual compute nodes in a Hadoop cluster. This includes keeping up-to date with the ResourceManager (RM), overseeing containers’ life-cycle management; monitoring resource usage (memory, CPU) of individual containers, tracking node-health, log’s management and auxiliary services which may be exploited by different YARN applications.
- Main task: Job life-cycle management
ApplicationMaster (AM)¶
ApplicationMaster (AM) is for executing shell commands on a set of launched containers using the YARN framework. AM is started on a container by the ResourceManager’s launcher. The first thing that AM needs to do is to connect and register itself with the ResourceManager (RM). The registration sets up information within RM regarding what host:port AM is listening on to provide any form of functionality to a client as well as a tracking URL that a client can use to keep track of status/job history if needed. AM needs to send a heartbeat to RM at regular intervals to inform RM that it is up and alive.
- Main task: job scheduling, monitoring on a container
Check Status¶
HDFS:
hdfs dfsadmin -report
YARN:
yarn node -list
Web Interface¶
YARN ResourceManager:
8088Try to open a web browser with a master node address (IP or hostname):
http://[node address]:8088
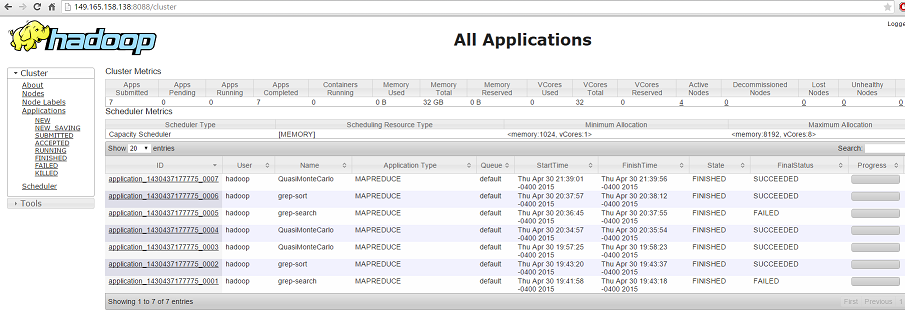
Figure 4. Overview of YARN GUI
YARN NodeManager:
50060This is for all slaves.
Citation¶
QnAs¶
- What if a cluster node goes down for any reason? How resources are relocated?
- A. When a node goes down, the corresponding containers including ApplicationMaster (AM) also get terminated. ResourceManager automatically restarts AM based on application policies and notifies the corresponding AMs to containers so that they can take further actions e.g. retry, kill application.
- Q. Is there a monitoring toolkit for resource allocation, cluster node, or entire cluster?
- A. There are several ways to monitor resource allocation using the client side RPC calls. Similar APIs exist for per node usage, cluster usage. See getApplicationReport(), getClusterNodes() and getClusterMetrics() APIs at http://hadoop.apache.org/docs/stable/api/org/apache/hadoop/yarn/api/ApplicationClientProtocol.html.
Useful Links¶
- Hadoop Cluster Setup: http://hadoop.apache.org/docs/current/hadoop-project-dist/hadoop-common/ClusterSetup.html
- WordCount v1.0: http://hadoop.apache.org/docs/current/hadoop-mapreduce-client/hadoop-mapreduce-client-core/MapReduceTutorial.html#Example:_WordCount_v1.0
- Hadoop 2.x installation: http://www.highlyscalablesystems.com/3597/hadoop-installation-tutorial-hadoop-2-x/
- pi Estimator: http://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/documentation/articles/hdinsight-sample-pi-estimator/
- Examples on Hadoop YARN: http://docs.hortonworks.com/HDPDocuments/HDP2/HDP-2.1.3/bk_using-apache-hadoop/content/running_mapreduce_examples_on_yarn.html
YARN Vendors¶
Cloudera and Hortonworks are major vendors of Hadoop. They provide helpful documentation about Hadoop developments.